Distance From Shortest To Longest
Accept you ever thought about the reason why humans are capable of seeing colours? The reason is, colours are nothing merely electromagnetic radiation with a different wavelength of light. In the electromagnetic spectrum, the visible region is otherwise called visible calorie-free. These colours have different wavelengths too. In this article, let us acquire what is wavelength and wavelength of visible light in particular.
What is Wavelength?
The wavelength of light is defined as "The distance between the two successive crests or troughs of the light moving ridge". It is denoted past the Greek letter lambda (λ). Therefore, the distance betwixt either one crest or trough of i wave and the side by side wave is known as wavelength.
What is Visible Spectrum?
The visible spectrum is cypher only the observable region of the electromagnetic wave which is visible to human eyes. In the electromagnetic spectrum, the visible spectrum ranges from the infrared region to the UV region. The visible light lies in between the infrared and ultraviolet range of wavelengths. The human center tin can detect the calorie-free spectrum ranging from 400 nanometers (violet) to about 700 nanometers (red). Other electromagnetic radiations are either as well small or too large to capture for the homo heart and are out of biological limitations.
We can see these waves as the colours of the rainbow where each colour includes a different wavelength. In the visible light, we tin can as well see the dominicus'due south outermost layer – the corona.
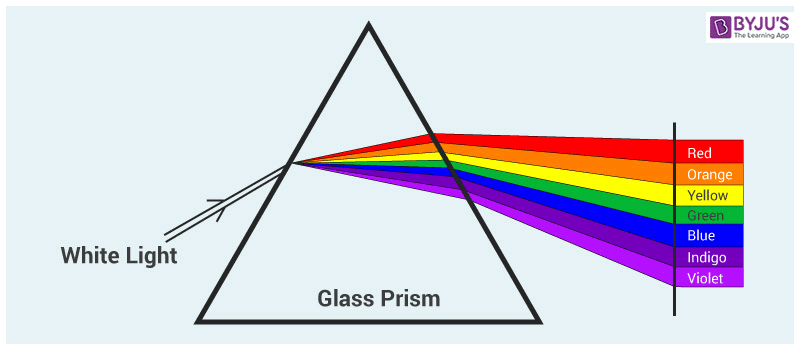
When the visible light travels through a prism, the visible calorie-free gets separated into a spectrum of colours. Red color has the longest wavelength of 700 nm, and violet has the shortest wavelength of 380 nm. These colours adjust themselves according to the wavelength as the spectrum of rainbow colours.
How is the Wavelength of Low-cal Calculated?
Every bit light has the properties of a wave and a particle, it can be expressed in two equations:
\(\begin{assortment}{50}\nu =\lambda f\end{assortment} \)
\(\brainstorm{array}{50}E =hf\end{array} \)
Where,
- ν is the velocity of the light.
- λ is the wavelength of the low-cal.
- f is the frequency of the light.
- E is the energy of the light wave.
- h is the Planck'south Abiding ( 6.64 × 10-34 joule.second)
Hither, the showtime equation denotes the wave nature of the light and the second equation denotes the particle nature of the light.
Wavelength of Visible Light
- Wavelength of the Visible Light ranges from 400 nm to 700 nm and hither we come to know the wavelength of various colours of the visible spectrum of light.
- The spectrum of visible light has numerous unlike colours having different wavelengths.
- The violet colour is said to take the shortest form of wavelength whereas the red colour is said to have the longest wavelength.
- It tin can likewise be noticed in the below-given effigy.

The wavelength for various colours of the visible spectrum of light is provided in the tabular array underneath.
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
| | | |
Instance on Wavelength of Light
Calculate the wavelength of visible light whose frequency is 6.24 x 1014Hz
Ans: Given, Frequency of light = 6.24 x 10xivHz
We know, the velocity of light = 3 x 108 m/sec
Equally per the formula of the wavelength of lite,
\(\begin{array}{l}\lambda =\frac{\nu }{f}\\ \\ \Rightarrow \lambda =\frac{3\times 10^{8}}10{6.24\times 10^{fourteen}}\\ \\ \Rightarrow \lambda = 4.80\times 10^{-7}\end{assortment} \)
Since wavelength is inversely proportional to the frequency, we tin empathise that the longer the wavelength of the calorie-free, the lower is the frequency. In the same manner, the shorter the wavelength, the higher will exist the frequency of the lite.
Also, larn the departure betwixt violet and imperial.
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
What happens to the frequency of the ray of calorie-free travelling from one medium to another?
The frequency of the ray of calorie-free remains the same when the ray of light is travelling from one medium to another.
What are the properties of light waves emitted by the laser?
Following are the backdrop of the light waves emitted by the laser:
- They take the same phase
- They have the same amplitude
- They have the same frequency
Why practise low-cal waves travel slower in drinking glass than in air?
The light waves travel slower in glass than in air because the density of the glass is greater than the density of the air.
State if the given argument is truthful or faux: Light cannot travel through a vacuum.
The given statement is false because light can travel through a vacuum. Lightwave beingness an electromagnetic wave, it does not need a medium to propagate.
What happens to the pattern obtained during diffraction if monochromatic light is replaced by the white calorie-free?
When the white lite replaces monochromatic light, a coloured pattern is observed along with a white fringe at the centre. Also, the clarity of the band will exist lost as in that location will be overlapping of the coloured bands.
Promise you have understood about wavelength of light and wavelength of visible light. Stay tuned with BYJU'S for more such interesting articles. Too, register to "BYJU'S – The Learning App" for loads of interactive, and engaging Physics-related videos.
Distance From Shortest To Longest,
Source: https://byjus.com/physics/wavelength-of-light/
Posted by: doryortherce.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Distance From Shortest To Longest"
Post a Comment